Description
Given an m x n matrix of positive integers representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevation map, compute the volume of water it is able to trap after raining.
Note: Both m and n are less than 110. The height of each unit cell is greater than 0 and is less than 20,000.
Example
Given the following 3x6 height map:
[
[1,4,3,1,3,2],
[3,2,1,3,2,4],
[2,3,3,2,3,1]
]
Return 4.
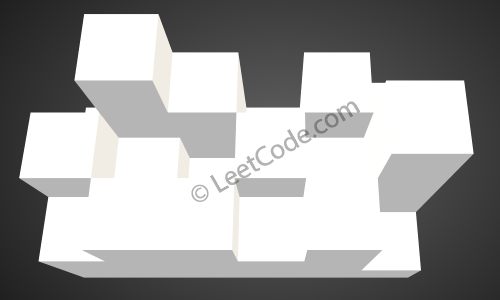
The above image represents the elevation map [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] before the rain.
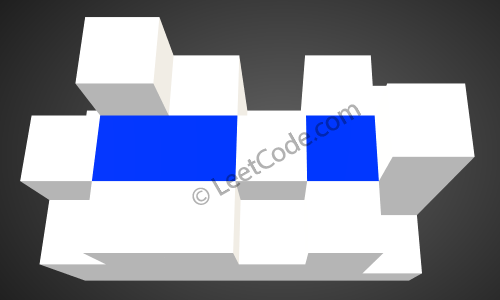
After the rain, water is trapped between the blocks. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
Discussion
这个问题是凹槽盛水问题的3D版本,但是解乏确实完全不同。
这个问题可以采用模拟海平面上升的解法。思路如下:
-
首先将四周一圈的点加入优先队列pqueue,并标记为已访问。
-
从优先队列取出最矮的点。对这个点上下左右四个方向进行访问(不能超过边界,不能是已访问的点)并加入优先队列,如果新点比该点的地势低,那么说明水可以灌进去,那么我们就把水灌进去到和该点平齐的高度,并统计灌入水的量,然后把新点加入优先队列。
-
当pqueue没有点时,结束。
这个方法就类似于在周围不停灌水,看有多少水能流到凹槽中去。
算法的时间复杂度为O(n)。
C++ Code
class Solution {
public:
int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& heightMap) {
if (heightMap.size() < 3 || heightMap[0].size() < 3) {
return 0;
}
int trapped_rain = 0;
int row = heightMap.size();
int col = heightMap[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> visited(row, vector<bool>(col, false)); //记录该处是否被访问过
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> pqueue; //优先队列
vector<vector<int>> dir = {
{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}
}; //上下左右四个方向
//初始把四周边界上的点加入优先队列。
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (i == 0 || i == row - 1 || j == 0 || j == col - 1) {
visited[i][j] = true;
pqueue.push({heightMap[i][j], i * col + j});
}
}
}
while (!pqueue.empty()) {
pair<int, int> tmp = pqueue.top();
pqueue.pop();
int tmp_height = tmp.first;
int tmp_row = tmp.second / col;
int tmp_col = tmp.second % col;
for (int i = 0; i < dir.size(); i++) {
int new_row = tmp_row + dir[i][0];
int new_col = tmp_col + dir[i][1];
if (new_row > 0 && new_row < row && new_col > 0 && new_col < col && visited[new_row][new_col] == false) { //只访问未访问过的点
if (heightMap[new_row][new_col] < heightMap[tmp_row][tmp_col]) {
trapped_rain += tmp_height - heightMap[new_row][new_col];
heightMap[new_row][new_col] = tmp_height;
}
visited[new_row][new_col] = true;
pqueue.push({heightMap[new_row][new_col], new_row * col + new_col});
}
}
}
return trapped_rain;
}
};